The Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Center for Microeconomic Data today issued its Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit. The Report shows an increase in total household debt in the third quarter of 2022, increasing by $351 billion (2.2%) to $16.51 trillion. Balances now stand $2.36 trillion higher than at the end of 2019, before the pandemic recession. The report is based on data from the New York Fed’s nationally representative Consumer Credit Panel.
Mortgage balances rose by $282 billion in the third quarter of 2022 and stood at $11.67 trillion at the end of September, representing a $1 trillion increase from the previous year. Credit card balances also increased by $38 billion. The 15% year-over-year increase in credit card balances represents the largest in more than 20 years. Auto loan balances increased by $22 billion in the third quarter, consistent with the upward trajectory seen since 2011. Student loan balances slightly declined and now stand at $1.57 trillion. In total, non-housing balances grew by $66 billion.
Mortgage originations, which include refinances, stood at $633 billion in the third quarter, representing a $126 billion decline from the second quarter and a return to pre-pandemic volumes. The volume of newly originated auto loans was $185 billion, a slight reduction from the previous quarter but still elevated compared to the average volumes seen through the 2018-2019 period. Aggregate limits on credit card accounts increased by $82 billion and now stand at $4.3 trillion.
“Credit card, mortgage, and auto loan balances continued to increase in the third quarter of 2022 reflecting a combination of robust consumer demand and higher prices,” said Donghoon Lee, Economic Research Advisor at the New York Fed. “However, new mortgage originations have slowed to pre-pandemic levels amid rising interest rates.”
emphasis added

Here are three graphs from the report:
The first graph shows aggregate consumer debt increased in Q3. Household debt previously peaked in 2008 and bottomed in Q3 2013. Unlike following the great recession, there wasn’t a huge decline in debt during the pandemic.
From the NY Fed:
Aggregate household debt balances increased by $351 billion in the third quarter of 2022, a 2.2% rise from 2022Q2. Balances now stand at $16.51 trillion and have increased by $2.36 trillion since the end of 2019, just before the pandemic recession.
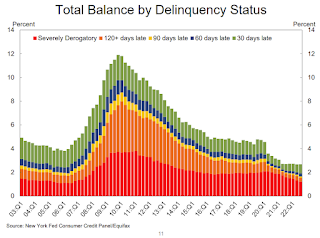
The overall delinquency rate was unchanged in Q3. From the NY Fed:
Aggregate delinquency rates were unchanged in the third quarter of 2022 and remained very low, after declining sharply through the beginning of the pandemic. As of September, 2.7% of outstanding debt was in some stage of delinquency, a 2.1 percentage point decrease from the last quarter of 2019, just before the COVID-19 pandemic hit the United States
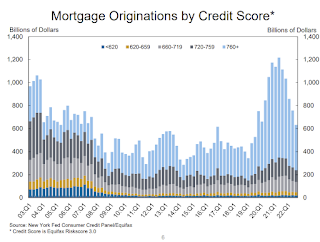
From the NY Fed:
Mortgage originations, measured as appearances of new mortgages on consumer credit reports, declined to $633 billion in 2022Q3, ending the period of high volumes of origination through the pandemic. … The median credit score of newly originated mortgages declined again, to 768, down from a series high in 2021Q1 of 788 and returning to pre-covid levels which remain very high and reflect continuing high lending standards.
There is much more in the report.