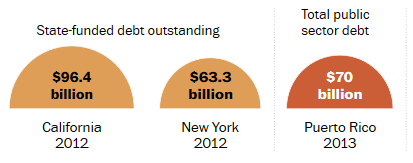
Puerto Rico has been in recession for 8 years. The unemployment rate is 15% and debt has piled up to the tune of $70 billion. For Comparison purposes, California public debt is $96 billion and Detroit debt was $18 billion. Wall Street rates Puerto Bonds at one step above junk.
How did Puerto Rico get into trouble? The short answer is the same way as Detroit: loss of industry coupled with lavish pensions.
The Washington Post reports Puerto Rico confronts a rising economic misery.
Boxes and wooden crates filled with household items bound for the U.S. mainland are stacked high in the Rosa del Monte moving company’s cavernous warehouse, evidence of the historic rush of people abandoning this beautiful island.
The economy here has been in recession for nearly eight years, crimping tax revenue and pushing the jobless rate to nearly 15 percent. Meanwhile, the government is burdened by staggering debt, spawning comparisons to bankrupt Detroit and forcing lawmakers to severely slash pensions, cut government jobs and raise taxes in a furious effort to avert default.
Officials in San Juan and Washington are adamant that a federal bailout is not on the table, but the situation is being closely monitored by the White House, which recently named an advisory team to help Puerto Rican officials navigate the crisis.
The island’s problems have ignited an exodus not seen here since the 1950s, when 500,000 people left for jobs on the mainland. Now Puerto Ricans, who are U.S. citizens, are again leaving in droves.
Puerto Rico lost 54,000 residents — 1.5 percent of its population — between 2010 and 2012 alone. Since recession struck in 2006, the population has shrunk by more than 138,000 to 3.7 million, with the vast majority of the outflow headed to the mainland.
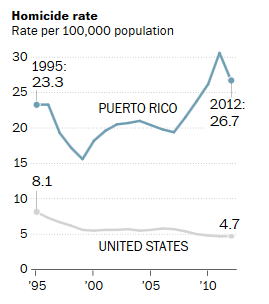
The brutal combination of a long recession, a shrinking population and overwhelming debt has left Puerto Rico’s political leaders struggling to manage a conundrum: How do they tame at least $70 billion in debt while marshaling the resources to grow a shrinking economy and battle corrosive social problems, including a homicide rate that is nearly six times the U.S. average?
Like states, the commonwealth of Puerto Rico cannot file for bankruptcy. Also, Puerto Rico’s constitution offers bondholders strong guarantees that they would be paid before pensioners and public workers if the government went broke.
Puerto Rico’s expansive web of debt includes standard government bonds as well as those floated by public corporations, including authorities for water and sewer, highways and electric power. Together, those bills have nearly tripled since 2000, as successive administrations turned to the bond market to plug gaping budget deficits. In addition to the $70 billion in government debt, the government also faces $37 billion in unfunded pension obligations, according to Morningstar.
Since 1996, the number of factory jobs in Puerto Rico plummeted from 160,000 to 75,000.
And while government workers make up about a quarter of the commonwealth’s workforce — much higher than the U.S. average of 16 percent — their ranks are shrinking as the pervasive debt and economic problems careen toward a reckoning. Now, just over 41 percent of working-age Puerto Ricans are in a job or even looking for one.
As work has disappeared, more Puerto Ricans have relied on the government to survive: About a third of the commonwealth’s population relies on food stamps, and residents of the island are twice as likely as those on the mainland to receive Social Security disability benefits, according to researchers.
Public Debt
Municipal Bankruptcies
Homicide Rate
Expect Default
Job flight, high crime rates, and huge pension woes in Puerto Rico seem similar to the problems in Detroit. However, there is no constitutional provision that allows US states and Commonwealths to declare bankruptcy.
Compounding the problem, Puerto Rico passed a massive set of tax hikes including corporate taxes, a broadened sales tax and a new gross receipts levy, hoping to get its budget under control. Given that tax hikes in the middle of a recession are about the worst possible choice, the situation is ominous.
So how is Puerto Rico’s debt going to be paid back? The answer is it won’t. Although, bankruptcy is out of the question, nothing can stop a default except a bailout by the US. Given that handouts from this Republican Congress are unlikely, look for Puerto Rico to default.
Mike “Mish” Shedlock
http://globaleconomicanalysis.blogspot.com